CNC plasma cutter: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|Name= CNC plasma cutter | |Name= CNC plasma cutter | ||
|Status=Initializing | |Status=Initializing | ||
|Contact= Walter | |Contact= Walter, [[User:Smeding|Smeding]], [[User:Gori|Gori]], [[User:Yotson|Yotson]], [[User:Semafoor|Semafoor]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
This goal is still a while away for now, but as always, we are full of Ideas and this is a convenient place to put them. | This goal is still a while away for now, but as always, we are full of Ideas and this is a convenient place to put them. | ||
== | == System overview == | ||
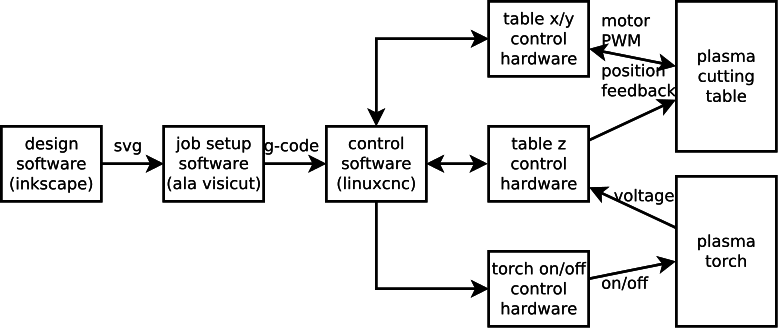
The diagram below shows the proposed system setup. | |||
[[File:plasmacnc.svg]] | |||
[[ | |||
From left to right: | |||
* design software (like inkscape) is used to design the shape to be cut and to export it as svg. | |||
* job setup software (unknown, but something like visicut) is used to position the shape and convert it to g-code. | |||
* linuxcnc (or possibly grbl) is used to "execute" the g-code through the control hardware. | |||
* the control hardware powers the motors of the cutting table and controls the plasma torch | |||
We're basing this project on an old X-Z traversing unit originally made for measuring air velocity distributions in wind tunnels at a metrology institute. The current motor controllers, however, seem to be made for a fixed speed and it's probably easiest to replace the electronics altogether. | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:X-Z_traverseerunit_front.jpg|X-Z traversing unit before any modifications | |||
File:X-Z_traverseerunit_stuurelektronika.jpg|Current control electronics with DC-motor controllers and Mitsubishi PLC | |||
</gallery> | |||
A Z-axis seems required to control the torch height. It won't need to move very far, quickly or precisely, though. | |||
* | == To-do list == | ||
# Decide how to control the machine. There seem to be two basic options: GRBL and LinuxCNC | |||
#* [[User:Smeding|Smeding]] knows a little bit about LinuxCNC and is willing to do some of the work | |||
# Design and build interface/driver hardware for motors and encoders | |||
#* [[User:Smeding|Smeding]] is willing to help with this | |||
#* [[Benadski]] has motor controller hardware that takes PWM as input. | |||
# Set up a PC that can withstand the general environment of the SparkShack (EMI, humidity, temperature) | |||
# Get basic motion control working so that the machine moves | |||
# Design and build interface hardware for the plasma torch, so it can be turned on and off. Will probably want voltage sensing for torch height control. | |||
#* [[User:Smeding|Smeding]] is willing to help with this, too | |||
# Add a third axis to the machine for torch height control | |||
# Put everything together -- implement the software side of things for torch height control and reading e.g. SVG files | |||
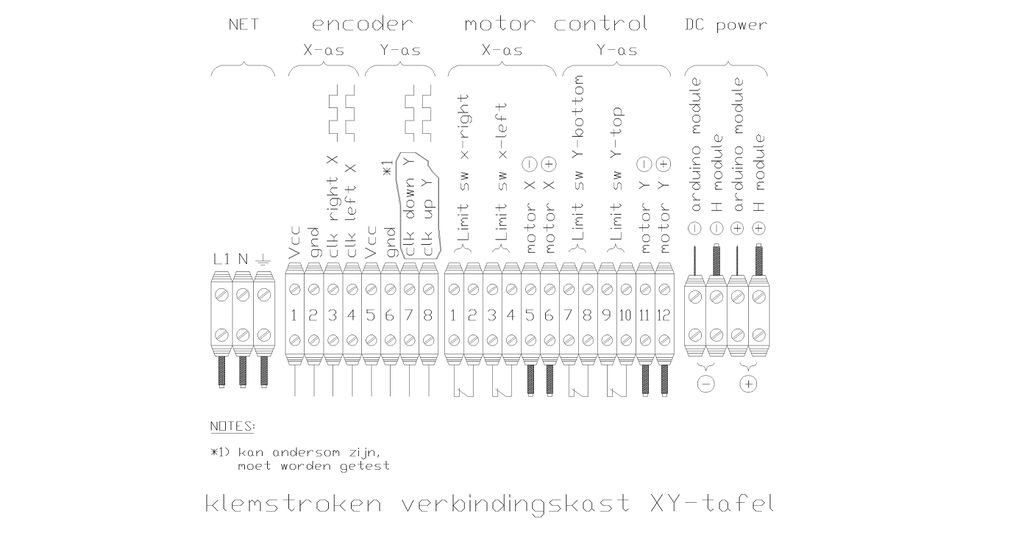
connection diagram: | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:XY-tafel connection diagram bewerkt.JPG|1024px]] | |||
<br> | |||
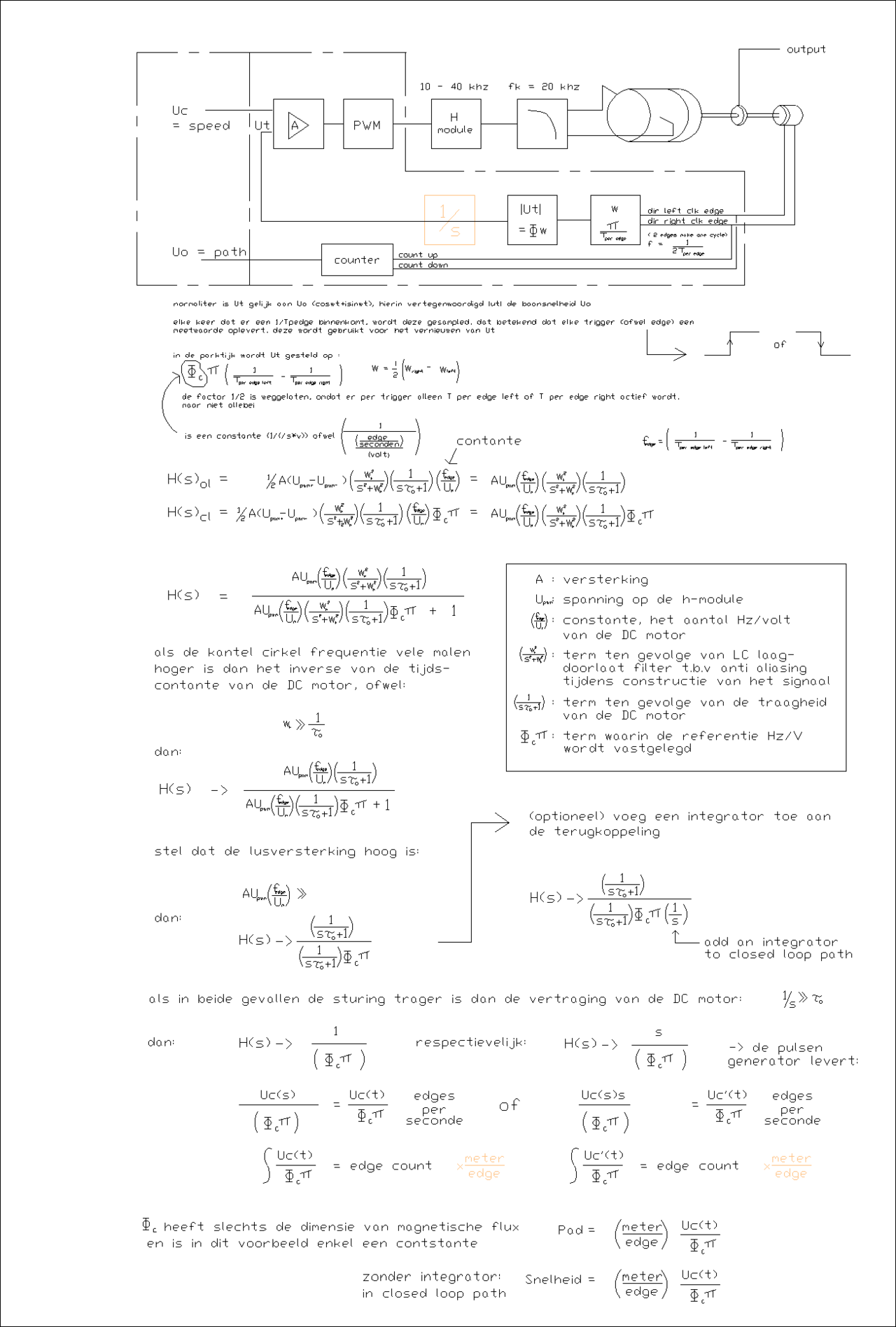
blokdiagram sturing plasmasnijder<br> | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:Blockdiagram sturing rev 2.1.PNG|1280px]] | |||
<br> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:43, 21 October 2015
| Project CNC plasma cutter | |
|---|---|
| Status | Initializing |
| Contact | [[Project Contact::Walter, Smeding, Gori, Yotson, Semafoor]] |
| Last Update | 2015-10-21 |
After acquiring a plasma cutter at the space, it seemed only logical to try and fabricate a CNC version eventually.
This goal is still a while away for now, but as always, we are full of Ideas and this is a convenient place to put them.
System overview
The diagram below shows the proposed system setup.
From left to right:
- design software (like inkscape) is used to design the shape to be cut and to export it as svg.
- job setup software (unknown, but something like visicut) is used to position the shape and convert it to g-code.
- linuxcnc (or possibly grbl) is used to "execute" the g-code through the control hardware.
- the control hardware powers the motors of the cutting table and controls the plasma torch
We're basing this project on an old X-Z traversing unit originally made for measuring air velocity distributions in wind tunnels at a metrology institute. The current motor controllers, however, seem to be made for a fixed speed and it's probably easiest to replace the electronics altogether.
-
X-Z traversing unit before any modifications
-
Current control electronics with DC-motor controllers and Mitsubishi PLC
A Z-axis seems required to control the torch height. It won't need to move very far, quickly or precisely, though.
To-do list
- Decide how to control the machine. There seem to be two basic options: GRBL and LinuxCNC
- Smeding knows a little bit about LinuxCNC and is willing to do some of the work
- Design and build interface/driver hardware for motors and encoders
- Set up a PC that can withstand the general environment of the SparkShack (EMI, humidity, temperature)
- Get basic motion control working so that the machine moves
- Design and build interface hardware for the plasma torch, so it can be turned on and off. Will probably want voltage sensing for torch height control.
- Smeding is willing to help with this, too
- Add a third axis to the machine for torch height control
- Put everything together -- implement the software side of things for torch height control and reading e.g. SVG files